Table of Contents
Tolvaptan is a vasopressin receptor antagonist, specific for the V2 receptor. This impairs urinary concentration and increases water excretion. Tolvaptan is classified as an aquaretic. In contrast to diuretics, aquaretics stimulate water excretion without significant electrolyte loss.
What is Vasopressin?
Vasopressin is the same thing as antidiuretic hormone (ADH).
It is a hormone that is secreted in the hypothalamus and stored in the posterior pituitary gland. Stimuli for vasopressin release can be:
- Osmotic. This is the main stimulus. An increase in plasma osmolarity is sensed by osmoreceptors. This occurs with hypernatremia (dehydration) appropriately signaling the kidney to reabsorb water.
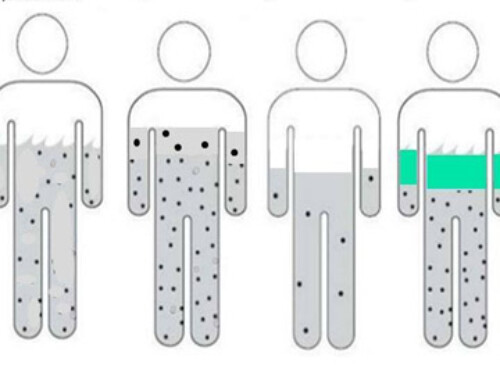
- Hemodynamic. The other “appropriate” stimulus. Occurs with true hypovolemia or decreased effective arterial volume (intravascular volume depletion) as occurs in heart failure and cirrhosis. Helps to maintain intravascular volume.
- Inappropriate. Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH). Occurs with central nervous system (CNS) or pulmonary disorders, malignancies and with certain medications.
Vasopressin acts on the vasopressin receptor. There are 3 vasopressin receptor subtypes.
- V1a – Located on vascular smooth muscle cells. Contribute to vasoconstriction when activated.
- V1b – Regulates the hypothalamic – pituitary – adrenal access, maintaining ACTH and corticosterone
- V2 – Located on the apical membrane of collecting duct cells in the kidney. Activation leads to an increase in cyclic AMP (cAMP). This stimulates the insertion of aquaporin channels in the basolateral membrane. This leads to water reabsorption resulting in a concentrated urine and a decrease in serum Na+.
Blocking the V2 receptor will prevent insertion of the aquaporin channel, inhibiting the reabsorption of water resulting in a concentrated urine, making it a treatment for hyponatremia.
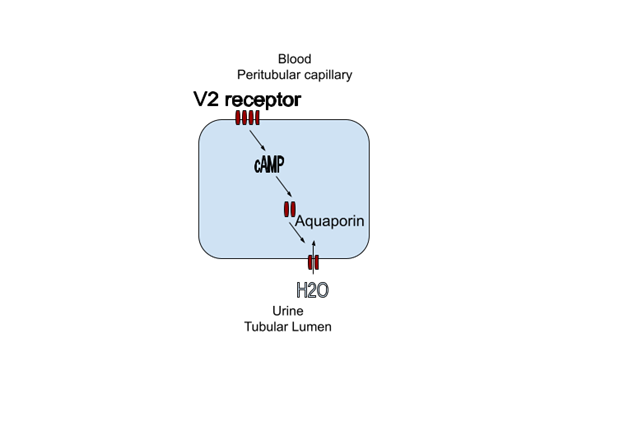
cAMP also stimulates cyst growth in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD). Blocking the V2 receptor can decrease cyst growth in this condition.
Tolvaptan Use in Hyponatremia
Tolvaptan is indicated for euvolemic and hypervolemic hyponatremia.
Euvolemic Hyponatremia.
- Typical dose 7.5 – 30 mg day
The SALT trials studied patients with euvolemic and hypervolemic hyponatremia.
Tolvaptan, a selective oral vasopressin V2-receptor antagonist, for hyponatremia – PubMed
- Approximately 60% had euvolemic hyponatremia, mainly SIADH.
- Studied tolvaptan vs placebo for 30 days.
- Initial dose 15 mg with protocol uptitration to 30 and 60 mg for slow correction.
- Increase in sodium evident by 8 hrs
- Mean increase
- Day 4 – 5.4 mEq/L (placebo 1 mEq/L)
- Day 30 – 7.2 mEq/L (placebo 2.3 mEq/L)
- Overly rapid correction (> 0.5 mEq/L per hour) was rare (1.8%)
Other metaanalysis and registries have shown an increase in sodium from 4-5.7 mEq/L with tolvaptan
Other studies have shown higher rates of overcorrection, with an incidence of correction > 8 mEq/L within 24 hours as high as 33%
Hypervolemic Hyponatremia
Congestive Heart Failure
- Approximately 30% of patients in the above SALT trial had congestive heart failure (CHF)
- EVEREST Effects of oral tolvaptan in patients hospitalized for worsening heart failure: the EVEREST Outcome Trial – PubMed
- Tolvaptan 30 mg daily for > 60 days
- Mean Na+ increase at 7 days 5.49 mEq/L (placebo 1.85 mEq/L)
- Improved weight and dyspnea vs. placebo
- No difference in other primary and secondary cardiovascular outcomes
Cirrhosis
- There is a FDA warning against use of tolvaptan in liver disease as LFT abnormalities were found in polycystic kidney disease (PKD) trials.
- However, it is effective in cirrhosis.
Tolvaptan treatment improves survival of cirrhotic patients with ascites and hyponatremia – PMC
When Not to Use Tolvaptan
Tolvaptan should not be used in the following circumstances
- Hypovolemic hyponatremia: In this situation tolvaptan may worsen intravascular volume depletion
- Severe acute symptomatic hyponatremia: In this case the sodium should be increased urgently by 4-6 mEq/L to decrease cellular swelling and decrease risk of severe CNS complications. The increase in sodium with tolvaptan is not quick or predictable enough to achieve this. 3% saline should be used instead.
My Practice. How I Use Tolvaptan in Hyponatremia
- Short term in hospitalized patients with moderate to severe asymptomatic hyponatremia refractory to conventional measures such as fluid restriction, loop diuretics and/or urea. (Have only rarely required chronic use post hospitalization)
- Monitor for overly rapid correction
- Check Na+ 6 – 9 hours after initial dose
- Suspend fluid restriction initially (for 1st 12 – 24 hours) to mitigate against overly rapid correction. Fluid restriction can then be reintroduced if overly rapid correction has not occurred
- Hold loop diuretics initially (for 1st 12- 24 hours) to guard against intravascular hypovolemia
Tolvaptan Resistance
Resistance to tolvaptan has been described in up to 15% of patients. Reasons include
- Very high vasopressin levels may overwhelm the competitive antagonist effect. Typically in SIADH, vasopressin levels are not very high. They may be in the “normal” range, but inappropriate for the clinical content (hyponatremia).
- Decreased distal fluid delivery due to a decreased GFR or increased fluid reabsorption in the proximal tubule. If fluid doesn’t get to the site of action in the cortical collecting tubule blocking the V2 receptor won’t have an effect. This is seen in hypervolemic states and accounts for the decreased response than occurs in euvolemic states.
- Excessive water intake. This medication and underlying conditions are often associated with increased thirst.
- Nephrogenic syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis. This is a condition where there is a constitutively activating mutation of the V2 receptor resulting in aquaporin channels despite low or undetectable vasopressin levels.
Summary
Tolvaptan is a useful adjunct for refractory euvolemic or hypervolemic hyponatremia. It should not be used with hypovolemia or in acute symptomatic hyponatremia requiring urgent correction. Although effective in cirrhosis it is not approved in liver disease or for chronic use for hyponatremia. Close monitoring is required because of the risk of overly rapid correction.