What is your differential for nephrotic proteinuria?
First:
- Nephrotic proteinuria > 3.5 grams/ 24 hrs or random urine protein creatinine ratio >3.5 grams per gram
- Nephrotic syndrome: Nephrotic proteinuria with associated clinical manifestations of hypoalbuminemia, edema, hyperlipidemia
As mentioned here: Proteinuria What it is and How I Treat
Begin considering these diagnoses when proteinuria exceeds 1 gram on 24 hr urine or protein creatinine ratio is > 1000 mg/g.
The differential may seem overwhelming, but if you break it down there’s not a whole lot to remember. I like to divide into:
- Primary glomerular diseases
- Idiopathic
- Secondary (to systemic disease)
- Secondary glomerular diseases
Primary glomerular diseases
The primary glomerular diseases are based on the renal pathology. They may be idiopathic or secondary to systemic diseases, so there’s a further breakdown. The secondary glomerular diseases have nephropathology unique to the systemic condition.
There’s not too many to remember. Some only present with a nephritic picture, others may present either Nephrotic or Nephritic.
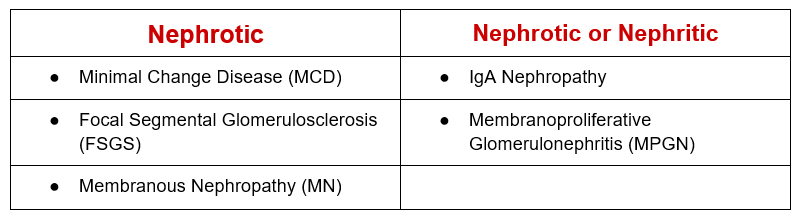
Systemic diseases
The systemic diseases have a distinct renal pathology. Break down between common and less common.
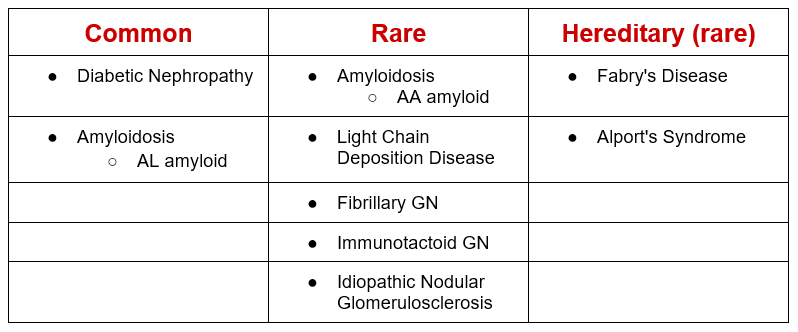
So, I kind of lied a bit for simplicity. The “distinct” nephropathology for diabetic nephropathy is nodular glomerulosclerosis. This appearance on light microscopy of kidney biopsy can also be seen in Light Chain Deposition Disease and Idiopathic Nodular Glomerulosclerosis.
Now for a deeper dive into the “primary” glomerular diseases and their “secondary” causes.
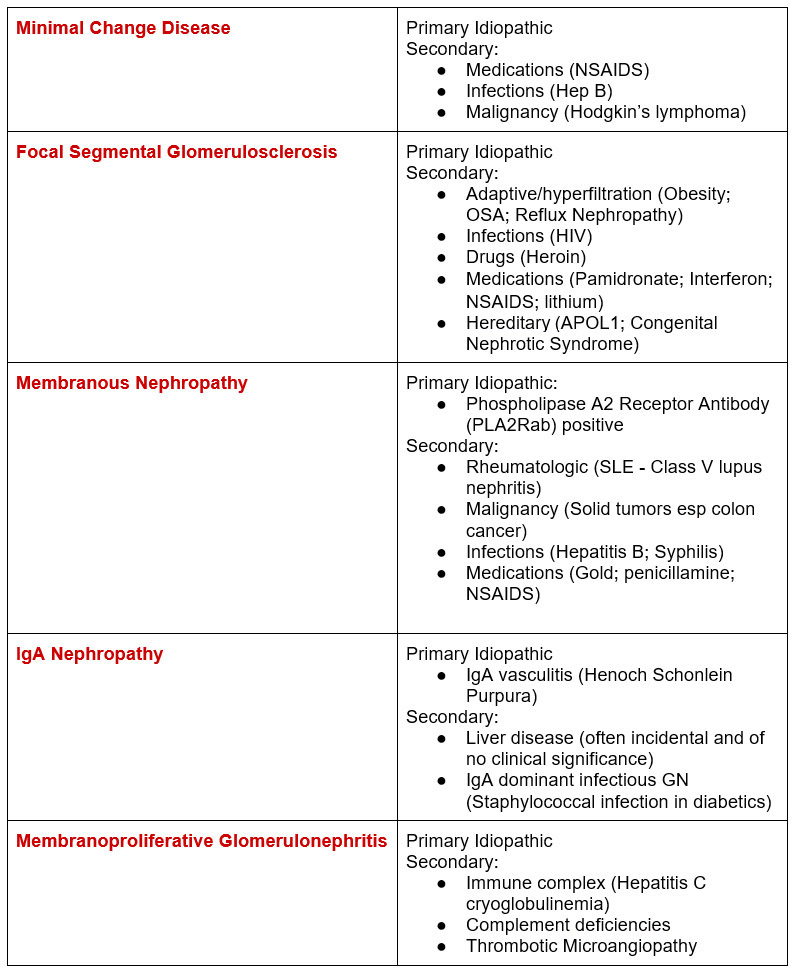
Serologic evaluation
Knowing the secondary causes and systemic conditions of nephrotic proteinuria defines the serologic workup.
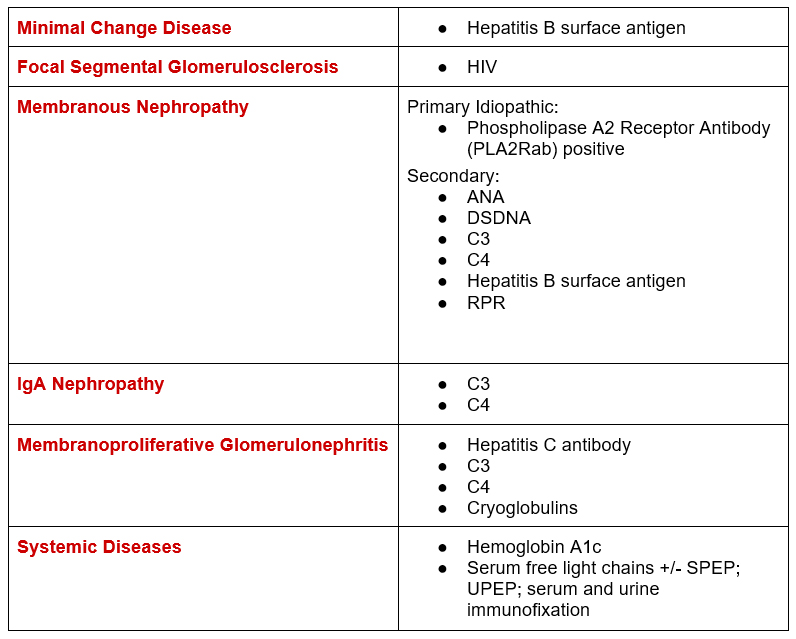
Synthesizing the serologies above a comprehensive serologic evaluation for nephrotic proteinuria. The highlighted ones are what I typically do as a baseline, the others depend on clinical situation.
- ANA
- C3
- C4
- Cryoglobulins (if Hepatitis C antibody positive, C4 low, or signs of systemic vasculitis)
- DS DNA (if ANA positive)
- Hg A1c (if elevated blood glucose)
- Hepatitis B Surface Antigen
- Hepatitis C Antibody
- HIV (if risk factors)
- Phospholipase A2 receptor antibody (PLA2R ab)
- RPR (if risk factors)
- Serum free light chains (+/- SPEP, UPEP, serum and urine immunofixation)
What you don’t see on this list, don’t check these unless nephritic picture
- Anti Glomerular basement membrane (GBM) antibody
- ANCA
- Proteinase 3 antibody
- Myeloperoxidase antibody
Summary
The differential for nephrotic proteinuria may seem overwhelming, but it is manageable if you can remember 7 (five + two) things:
Five primary glomerular pathologies:
- Minimal Change Disease (MCD)
- Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (FSGS)
- Membranous Nephropathy (MN)
- IgA Nephropathy
- Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis (MPGN)
Two systemic diseases: