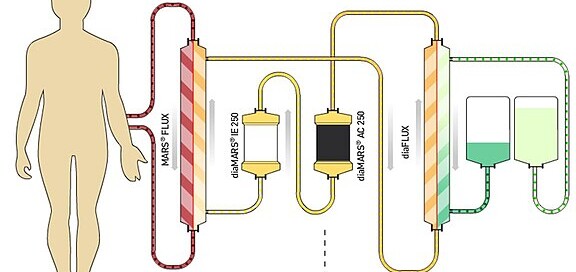
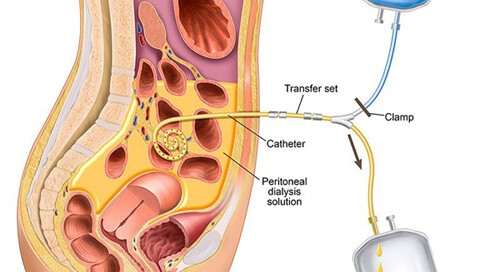
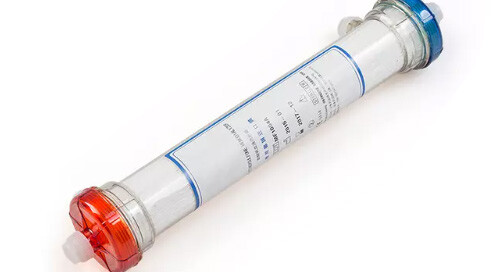
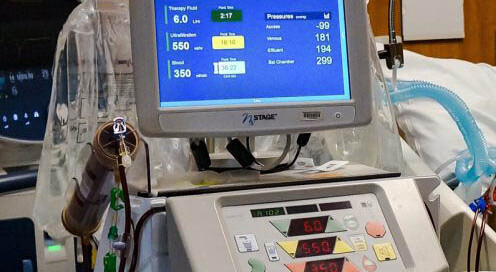
Dialysis for Liver Failure?
Is there a role for dialysis in acute liver failure? Hepatic failure can be associated with acute kidney injury and dialysis may be indicated in these situations, that’s not what this article will address. Instead we will explore a role for dialysis in acute liver failure even if there is not kidney failure.