Table of Contents
There are 3 available mineralocorticoid antagonists (MRAs)
- Spironolactone: This is a steroidal MRA derived from steroids that is nonselective for the mineralocorticoid (MR) receptor, it also can inhibit other steroid receptors specifically progesterone and androgen receptors
- Eplerenone: Is a second generation steroidal MRA that is more selective for the MR receptor, but less potent than spironolactone
- Finerenone: is a nonsteroidal MRA, and because it is nonsteroidal, is most selective for the MR receptor and is at least as potent as spironolactone.
This article will review how mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists work, differences between these three medications and how I use each in clinical practice.
How Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists Work
Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists work by… wait for it… blocking the mineralocorticoid receptors.
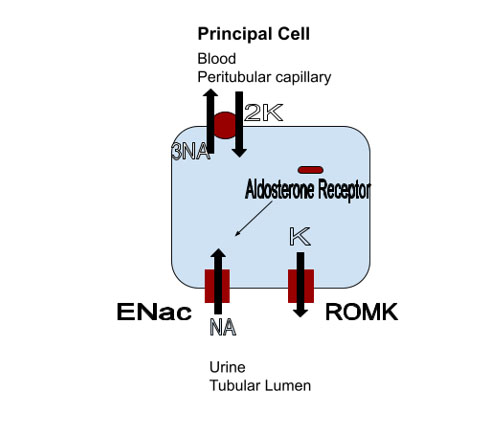
In the kidney mineralocorticoid receptors are located in the principal cell of the distal nephron. When activated by aldosterone they increase expression of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC). This channel is inserted in the luminal membrane of the cell leading to increased sodium reabsorption. The sodium reabsorption creates an electrochemical gradient for potassium secretion. The result is volume expansion tending to raise blood pressure and a decrease in plasma potassium.
Blocking the aldosterone receptor will lead to decreased ENaC expression leading to increased sodium and decreased potassium excretion. The end result tends to be a decrease in blood pressure and increase in plasma potassium.
Renal Benefits of Mineralocorticoid Antagonists
Based on the mechanism of action it is clear how MRA’s are beneficial in the treatment of HTN and hypokalemia and it should be intuitive that it would be beneficial in states of aldosterone excess such as primary hyperaldosteronism.
They also result in decreased urinary protein and progression of kidney disease by
- Decreasing glomerular pressure and
- Podocyte stress/damage and
- Renal inflammation and fibrosis mediated by aldosterone.
Differences in Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists
First, Spironolactone is nonselective, while eplerenone and finerenone are selective for the mineralocorticoid receptor. Because it is non selective and able to block progesterone and androgen receptors there can be side effects that are typically not seen with eplerenone or finerenone such gynecomastia, decreased libido and menstrual irregularities.
Next, Spironolactone and eplerenone are steroidal while finerenone is a nonsteroidal MRA. This makes finerenone the most selective for the MR receptor.
Eplerenone is metabolized by the cytochrome p450 system. Therefore there are drug interactions that may increase or decrease the levels of this medication.
Finally, Spironolactone and eplerenone are mainly distributed in the kidney while finerenone is equally distributed in the kidney and the heart. In addition finerenone is less lipophilic, has a relatively short half-life and does not have active metabolites. For these reasons finerenone is less likely to cause hyperkalemia and has less of an antihypertensive effect than spironolactone or eplerenone.
Hyperkalemia
Regarding hyperkalemia, there is a real risk of this with all of these medications (including finerenone) particularly since many of these patients will also be on a renin angiotensin system blocker. This needs to be monitored closely. My practice is to:
- Not initiate spironolactone or eplerenone if the potassium is >7. I would consider finerenone in this situation.
- Routinely check a basic metabolic panel bmp 1-2 weeks after initiation or a dose increase.
- Advise patients to avoid using additional medications that can raise the potassium, specifically Bactrim (TMP/SMX) and NSAIDS. If for some reason a short course of these other medications is necessary I advise the MRA to be held.
How I use Mineralocorticoid Antagonists
Spironolactone
Of these 3 medications, I use spironolactone most. This is because:
- It is generic, so cost is typically not an issue as it can be for finerenone
- It is more potent than eplerenone and
- I typically find benefit and do not need to go higher than the 25 mg dose. The adverse side effects of gynecomastia, decreased libido and menstrual abnormalities are uncommon at this dose.
I will use spironolactone for the following indications:
- Primary hyperaldosteronism: Primary Hyperaldosteronism | BCNephro How to Diagnose Primary Hyperaldosteronism @BCNephro
- Resistant HTN: https://bcnephro.com/hypertension-a-nephrologists-approach-2/ Hypertension a Nephrologist’s Approach @BCNephro particularly if hypokalemia or low/normal potassium. It is the go to 4th line agent after renin angiotensin system blocker, thiazide, dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker. Will use earlier if hypokalemia or intolerance of one of the other medications.
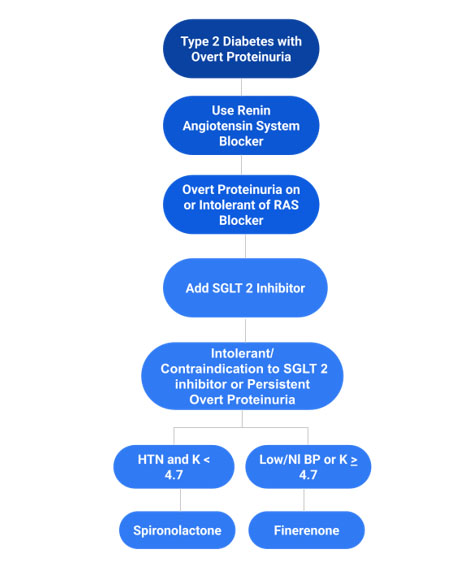
- Overt proteinuria: (UPCR > 500 mg/g, UACR > 300 mg/g) Proteinuria: What is it and How I Treat | BCNephro Proteinuria How I Treat @BCNephro in patients already on (or intolerant of) RAS blocker and HTN and normal potassium. If this patient had an elevated potassium or normal blood pressure I would preferentially use an SGLT 2 inhibitor.
- Hypokalemia, particularly if associated with HTN. If the BP is low or normal, amiloride would be my go to.
Eplerenone
I would use eplerenone in a patient with any of the above indications who was intolerant of spironolactone.
Finerenone
The Fidelio-DKD studied finerenone in patients with diabetic kidney disease on a renin angiotensin system blocker.
Inclusion criteria were Type 2 diabetes and:
- Microalbuminuria (urine albumin creatinine ratio 30-300 mg/g), retinopathy and an eGFR 25-60 ml/ min or
- Overt albuminuria (urine albumin creatinine ratio 300-5000 mg/g) and an eGFR 25-75.
It found with finerenone there was a:
- Decrease in urine albumin creatinine ratio by 31%
- Decreased progression of CKD defined as kidney failure, death from renal causes or a sustained decrease in eGFR by > 40% (17.8 vs 21.1%)
There were minimal effects on potassium and blood pressure
- Hyperkalemia requiring drug discontinuation 2.3%
- Decrease in systolic blood pressure of 2-3 mm/Hg
My niche for finerenone is in a patient with diabetic kidney disease who has overt proteinuria (UPCR > 500 mg/g; UACR > 300 mg/g) despite being on or intolerant/contraindication to a RAS blocker and SGLT2 inhibitor, who has low or normal blood pressure and high/normal potassium. If this patient had an elevated blood pressure and normal potassium I would preferentially use spironolactone.
How I treat Proteinuria in Type 2 Diabetes
Summary
Mineralocorticoid antagonists are important agents in the treatment of hypertension and proteinuric kidney disease. Spironolactone, eplerenone and finererone are the available agents, with differences in selectivity for the mineralocorticoid receptor, side effects, potency and effect on blood pressure and potassium.